SDR VS. HDR: The Things You Need to Know
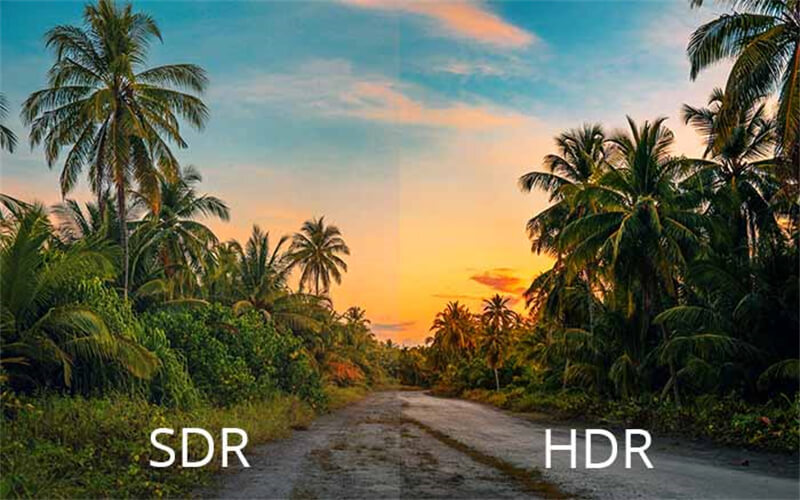

In recent years, there has been a remarkable growth in display technologies that have revolutionized our viewing experience. High Dynamic Range (HDR) technology has come up as a major player in this domain. Its promising enhanced color reproduction, improved contrast, and more immersive viewing experience has taken HDR TV to a new level. Today, as we delve into the world of HDR, it is crucial to read its key features and how it compares to Standard Dynamic Range (SDR). Thus, this article will explore the essentials of HDR technology and discover what you need to know about SDR vs. HDR.
So, read on as in the following parts, we shall see SDR vs. HDR, which is better, their definition, and their advantages in daily life.
Part 1: Definition of SDR and HDR
Before an HDR vs. SDR comparison, it is crucial to learn what they are. So, in the first part of this article, we will detail SDR HDR meaning along with their types.
What's SDR:
SDR, or Standard Dynamic Range, is an old display technology that has been in use for many years. It represents a standard range of brightness and colors reproducible on display. SDR is characterized by a limited contrast ratio and a narrower color gamut, resulting in a more modest visual experience than HDR.
Types of SDR:
There are two different types of SDR that you can use in various applications:
1. SDR Broadcast
This refers to the SDR standard used in traditional television broadcasting. It typically supports a color space known as Rec. 709, with a limited range of colors and brightness.
2. SDR Displays
SDR displays are standard in computer monitors, smartphones, and older television sets. These displays adhere to SDR broadcast's limited color space and often calibrate to provide consistent color reproduction.
What's HDR:
HDR, or High Dynamic Range, is a newer display technology that aims to overcome the limitations of SDR. It enables a more extensive range of brightness levels, a wider color gamut, and greater contrast ratios. HDR enhances the overall visual experience by delivering more vivid and lifelike images with improved details in bright and dark areas.
Types of HDR:
Four main kinds of HDR are currently being used or developed:
1. HDR10
HDR10 is the most widely adopted HDR format. It uses a 10-bit color depth, allowing for a peak brightness of 1,000 nits or higher. HDR10 is an open standard compatible with most HDR-capable displays and content providers.
2. Dolby Vision
Dolby Vision is a proprietary HDR format developed by Dolby Laboratories. It supports a higher dynamic range than HDR10, with a peak brightness of up to 10,000 nits. Dolby Vision also utilizes dynamic metadata, enabling scene-by-scene or even frame-by-frame adjustments for optimal image quality.
3. HLG (Hybrid Log-Gamma)
HLG is a backward-compatible HDR format developed by the BBC and NHK. It allows HDR content to be broadcasted alongside SDR content, enabling a smooth transition between the two for viewers with HDR and SDR-compatible devices.
4. Advanced HDR by Technicolor
This HDR format aims to provide enhanced color accuracy and fidelity. It utilizes a wide color gamut and advanced tone mapping techniques to deliver a visually stunning experience.
Please note that the choice of HDR format depends on the content creators, display manufacturers, and the specific requirements of the application or industry.
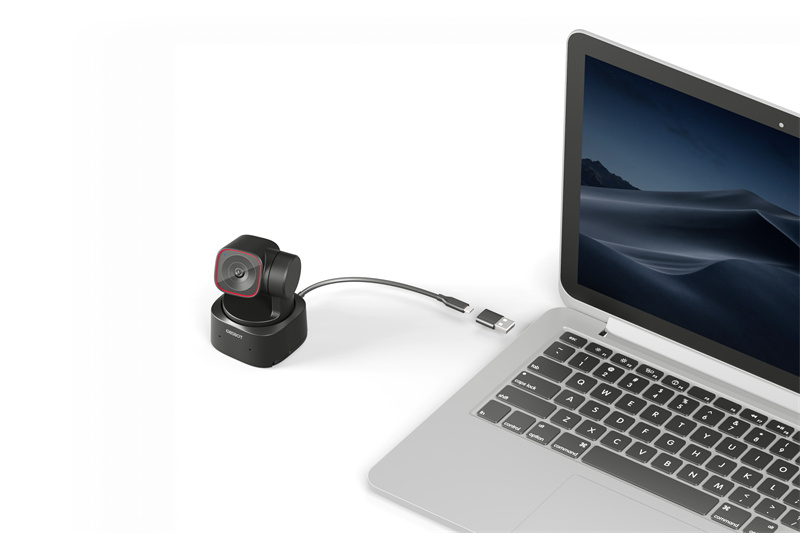
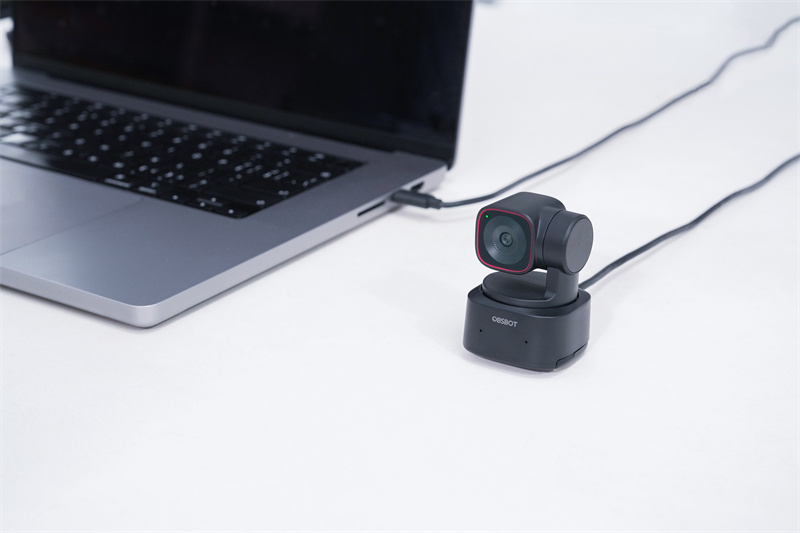
Bonus: The Best Webcam with HDR
If you're in need of a high-quality webcam that takes your visual experience a few steps ahead, we have none other than the OBSBOT Tiny 2. OBSBOT Tiny 2 is among the best webcams with its unique beauty mode, gesture and voice control advanced features, and HDR capabilities.
Key Features:
- HDR (High Dynamic Range): The OBSBOT Tiny 2 incorporates HDR technology, allowing it to capture and transmit video with exceptional clarity, color accuracy, and contrast. With HDR, you can enjoy vibrant, lifelike visuals that showcase the frame's darkest and brightest areas in stunning detail.
- 4K Resolution: The Tiny 2 boasts an impressive 4K resolution, delivering incredibly sharp and detailed video. So, when attending virtual meetings, streaming content, or recording videos, the high resolution ensures a professional-grade image quality that enhances your overall presentation.
- AI-Powered Tracking: One of the standout features of the OBSBOT Tiny 2 is its advanced AI-powered tracking. With built-in AI algorithms, the webcam can intelligently track and follow your movements, keeping you in the frame even if you're constantly moving around.
- Auto-Framing: The OBSBOT Tiny 2 offers auto-framing functionality, automatically adjusting the frame based on the number of people in the shot or predefined settings. This feature ensures that everyone in the frame remains visible and properly framed without requiring manual adjustments, making it ideal for group video calls and conferences.
- Hands-Free Voice Control: OBSBOT Tiny 2 supports hands-free voice control of a list of specified voice commands, like Track Me, Unlock Me, Sleep Tiny, Zoom In Closer, Zoom Out Further, Change Position, etc.
- Magical Gesture Control: This feature sports gesture control commands, like Dynamic Zoom in/out, Select/Cancel Target, and 4x Zoom In/Out.
Part 2: SDR vs. HDR: The Similarities and Differences
To understand which is better, HDR or SDR, it is advisable to understand the similarities and differences between these two resolutions.
Similarities of SDR and HDR
Despite their basic differences, SDR and HDR share similar basic display functionalities that include:
- Display Devices: You can view both SDR and HDR on various devices, including televisions, computer monitors, projectors, and mobile devices.
- Content Availability: Content is available in both SDR and HDR formats. However, HDR content is becoming increasingly prevalent, especially with the rise of streaming platforms and content providers offering HDR options.
- Connectivity: SDR and HDR content offer various connectivity options, such as cable, satellite, over-the-air broadcasting, streaming services, and physical media formats.
Now, let's explore the difference between HDR and non-HDR regarding quality, brightness, color gamut & volume, gradient, color depth, and internet speed requirements.
HDR vs SDR Comparison Table
| Aspect | SDR | HDR |
| Quality | Limited contrast and color reproduction | Enhanced contrast and color reproduction |
| Brightness | Standard range of brightness levels | Expanded range of brightness levels |
| Color Gamut & Volume | Narrower color gamut | Wider color gamut |
| Gradient | Limited ability to display subtle gradients | Improved gradient handling |
| Color Depth | 8-bit color depth | 10-bit or higher color depth |
| Internet Speed Requirement | Lower bandwidth requirements | Higher bandwidth requirements |
Thus, these differences result in a more visually immersive and lifelike experience with HDR, making it a sought-after technology for those seeking enhanced display capabilities.
Part 3: Is SDR Better than HDR?
No, the statement SDR is better than HDR is false since HDR offers several significant advantages over SDR. Thus, making it a preferred choice for many applications.
The main benefits of HDR
- Enhanced Visual Experience: HDR provides a more immersive and lifelike visual experience than SDR. HDR displays with a broader range of brightness levels and an excellent color gamut can reproduce more vivid and accurate colors, deeper blacks, and brighter highlights, resulting in images that closely resemble real-world scenes.
- Improved Contrast: HDR displays offer a higher contrast ratio, allowing for a more noticeable distinction between an image's darkest and brightest areas. This enhanced contrast enhances the depth and detail in shadows and highlights, resulting in a more dynamic and engaging visual experience.
- Greater Color Accuracy: HDR technology enables displays to reproduce a broader range of colors with greater precision and accuracy. This expanded color gamut allows for more vibrant and nuanced color reproduction, ensuring the visuals are accurate to the original content creator's intentions.
- Exemplary Gradient Handling: HDR excels at handling subtle gradients and smooth transitions between colors, minimizing color banding or visible steps. This capability ensures the visual content appears smoother and more natural, especially in scenes with gradual color changes or gradients.
- Higher Bit Depth: HDR supports higher color bit depths, typically 10 bits or higher, compared to the 8-bit color depth of SDR. This higher bit depth enables a more extensive range of color shades and gradations, resulting in smoother color transitions and reducing the likelihood of visible color banding.
- Future-Proof Technology: With the increasing availability of HDR content and HDR-compatible displays, HDR is rapidly becoming the standard for visual media. By investing in HDR technology, users can future-proof their viewing experience and ensure compatibility with upcoming content releases.
The above advantages make HDR the preferred choice for display quality and immersion.
Part 4: FAQs about SDR and HDR
Q1: How Do I Change from SDR to HDR?
To change from SDR (Standard Dynamic Range) to HDR (High Dynamic Range), you need the following:
- HDR-capable Display: Ensure you have an HDR-compatible display, such as an HDR TV or monitor, that supports HDR content playback.
- HDR Content Source: Obtain HDR content from compatible sources, such as streaming services, Blu-ray discs, or video games labeled as HDR-compatible.
- Display Settings: Access your device's display settings and enable HDR mode. The setting may vary depending on your specific device and operating system. Consult the user manual or manufacturer's instructions for detailed steps.
Q2. What Is the Highest Quality HDR?
Dolby Vision is currently considered one of the highest-quality HDR formats. It offers a comprehensive dynamic range and supports a peak glow of up to 10,000 nits, resulting in exceptional visual quality and precise color reproduction. However, the perception of quality can also depend on other factors, such as the content itself, the display device, and the viewing environment.
Q3: Is My Setup Able to Display HDR Content?
If all these four factors align, then your setup should be able to display HDR content and provide an enhanced visual experience:
- Display Capability: Check if your display device supports HDR. Look for labels such as "HDR10," "Dolby Vision," or "HLG" on the device specifications or consult the manufacturer's documentation.
- Content Source: Ensure that the content you are trying to view is HDR-enabled. Look for HDR indicators or labels on the content source, such as streaming platforms, Blu-ray discs, or video game settings.
- Connectivity: Verify that your setup supports the necessary HDR connection standards, such as HDMI 2.0 or DisplayPort 1.4, commonly used for transmitting HDR content.
- System Requirements: Confirm that your device, such as a computer or gaming console, meets the hardware and software requirements for playing HDR content. This may include having compatible graphics cards, drivers, or operating systems.
Conclusion:
Thus, that was about SDR vs. HDR. We detailed SDR HDR meaning, their differences, types, and similarities. Besides, we listed the benefits of using HDR as it is the best technology of our time. Lastly, we also answered some common questions related to checking if your system supports HDR, what is its highest quality, and how to switch from SDR to HDR easily.
Also, remember to try our recommended HDR webcam, the OBSBOT Tiny 2, for the best visual and audio experience.